Embark on an Adventure: Explore Lake Victoria, Africa’s Largest Freshwater Lake in Tanzania
Imagine yourself standing on the shores of a vast expanse of water, stretching as far as the eye can see. The gentle breeze carries the fresh scent of the lake’s waters, and the sound of waves lapping against the shore creates a soothing melody. This is Lake Victoria, Africa’s largest freshwater lake, and it is a place of awe-inspiring beauty and rich biodiversity.
Located in East Africa and shared by the countries of Tanzania, Uganda, and Kenya, Lake Victoria is an iconic natural wonder. Covering approximately 59,947 square kilometers, it holds the distinction of being the largest lake on the African continent. Its sheer size and abundance of aquatic life make it a captivating destination for nature enthusiasts, adventurers, and those seeking a tranquil escape.
But Lake Victoria is more than just a picturesque setting. It has a fascinating history that dates back centuries. Named after Queen Victoria by the intrepid explorer John Hanning Speke, the lake has played a significant role in the region’s cultural heritage and economic development for generations.
The lake is teeming with wildlife, including a diverse range of fish species such as the famous cichlids. These colorful creatures have adapted to the unique environment of Lake Victoria and have become an integral part of its ecosystem. Their vibrant colors and intricate mating behaviors have fascinated scientists and nature lovers alike.
Moreover, Lake Victoria is not only a natural wonder but also a thriving hub of economic activity. Its rich fishing grounds sustain vibrant fishing communities and support a thriving fishing industry. The lake’s waters are teeming with fish, providing sustenance and livelihoods for thousands of people.
Additionally, Lake Victoria has become a popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world. Its serene beauty offers opportunities for boating, sport fishing, and wildlife viewing. The surrounding areas have developed tourist infrastructure, including hotels, resorts, and guided tours, to cater to the growing number of visitors.
Location and Geography of Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is located in the African Great Lakes region, primarily situated in Tanzania and Uganda, with a small portion extending into Kenya. It is the largest lake in Africa and the world’s largest tropical lake. Lake Victoria is geographically characterized by its irregular quadrilateral shape and deeply indented shores.
The lake is part of a shallow depression in the great plateau between the Western and Eastern Rift Valleys. It has a surface elevation of 1,135 m (3,724 ft) above sea level, an average depth of 40 m (130 ft), and a maximum depth of 81 m (266 ft). With a shoreline stretching over 2,000 miles (3,220 km), Lake Victoria is surrounded by diverse landscapes, including precipices, swamps, and islands.

Hydrology and Limnology of Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria, the largest freshwater lake in Africa, has a complex hydrology that sustains its water volume and connects it to the mighty Nile River. Understanding the hydrological processes and limnology of Lake Victoria is crucial for comprehending the intricate ecosystem dynamics and challenges it faces.
The Water Inflow
The primary source of water inflow to Lake Victoria is direct rainfall, which accounts for approximately 80% of its water supply. Rainfall in the catchment area around the lake provides a steady influx of fresh water, replenishing its volume throughout the year.
In addition to rainfall, the lake also receives water from various rivers and thousands of small streams. Among these, the Kagera River stands out as the largest contributor to Lake Victoria’s water inflow. Originating from the Burundi highlands, the Kagera River flows into the lake, adding to its overall water volume and sustaining its hydrological balance.
The Outflow to the Nile River
The Victoria Nile serves as the only outflow from Lake Victoria, connecting it to the Nile River, the longest river in the world. The Victoria Nile carries the water from the lake and merges with the Albert Nile, forming the White Nile. This confluence marks the beginning of the Nile River’s journey towards Sudan and Egypt, eventually emptying into the Mediterranean Sea.
Water Volume and Balance
Lake Victoria has a vast water volume that plays a significant role in the overall hydrology of the region. With a total volume of approximately 2,760 km3, the lake encompasses a substantial amount of water, sustaining various ecological processes and supporting surrounding communities.
The lake experiences an average annual precipitation of 117 km3, replenishing its water reserves. However, it also faces a considerable evaporation rate of 105 km3, resulting in a delicate water balance that affects its overall level and sustainability.
Hydrological Factors and Challenges
Several factors influence the hydrology and limnology of Lake Victoria, including climate change, dam construction, and pollution from urban and agricultural sources. Climate change can alter rainfall patterns and temperature variations, potentially impacting the lake’s water inflow and balance.
The construction of dams within the lake’s catchment area can affect the flow of water, altering the hydrological processes and potentially leading to changes in lake levels and water quality. Additionally, pollution from urbanization and agricultural activities can introduce harmful substances into the lake, posing a threat to its ecological integrity and water quality.
Biodiversity of Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is renowned for its extraordinary biodiversity, boasting a diverse array of over 200 fish species. A haven for aquatic life, this freshwater lake teems with unique and fascinating marine creatures. However, the delicate equilibrium of the lake’s ecosystem has been disrupted by the introduction of invasive species, most notably the Nile perch. This introduction, which occurred in the 1950s, has had a detrimental impact on the native fish species, leading to a decline in their abundance and diversity. The consequences have been dire, with many endemic cichlids, a species known for their vibrant colors and captivating behaviors, becoming extinct.
Efforts are now underway to restore and protect the biodiversity of Lake Victoria. These measures aim to mitigate the negative effects of invasive species and promote sustainable fishing practices that can help revive the lake’s once-thriving ecosystem. By focusing on conservation, ecologically responsible fishing techniques, and the preservation of native species, it is possible to reverse the damage inflicted upon this remarkable body of water.
Lake Victoria’s biodiversity is of immense value, not only from an ecological standpoint but also in terms of its economic significance. The lake’s fishery supports the livelihoods of thousands of people in the surrounding communities, serving as an essential source of income and sustenance. Thus, safeguarding the biodiversity of Lake Victoria is not only vital for the health of the ecosystem but also for the well-being of the people who depend on its resources.
| Key Points | Implications |
|---|---|
| The introduction of the Nile perch in the 1950s | Caused a decline in native fish species and the extinction of many endemic cichlids |
| Efforts to restore biodiversity | Aims to mitigate the impact of invasive species and promote sustainable fishing practices |
| Lake Victoria’s fishery | Provides livelihoods for thousands of people in surrounding communities |
Conservation and Environmental Challenges
Lake Victoria, the largest freshwater lake in Africa, is facing numerous conservation and environmental challenges. Overfishing, pollution from urban and agricultural sources, and the proliferation of invasive species pose significant threats to the delicate ecosystem of the lake.
Overfishing has led to a decline in fish populations, disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem. As the demand for fish continues to rise, unsustainable fishing practices have depleted certain fish species, causing a ripple effect throughout the food chain.
Pollution from urban areas, including untreated sewage and industrial waste, as well as runoff from agricultural activities, has contaminated the waters of Lake Victoria. This pollution not only affects water quality, but also harms the diverse marine life that depends on the lake for survival.
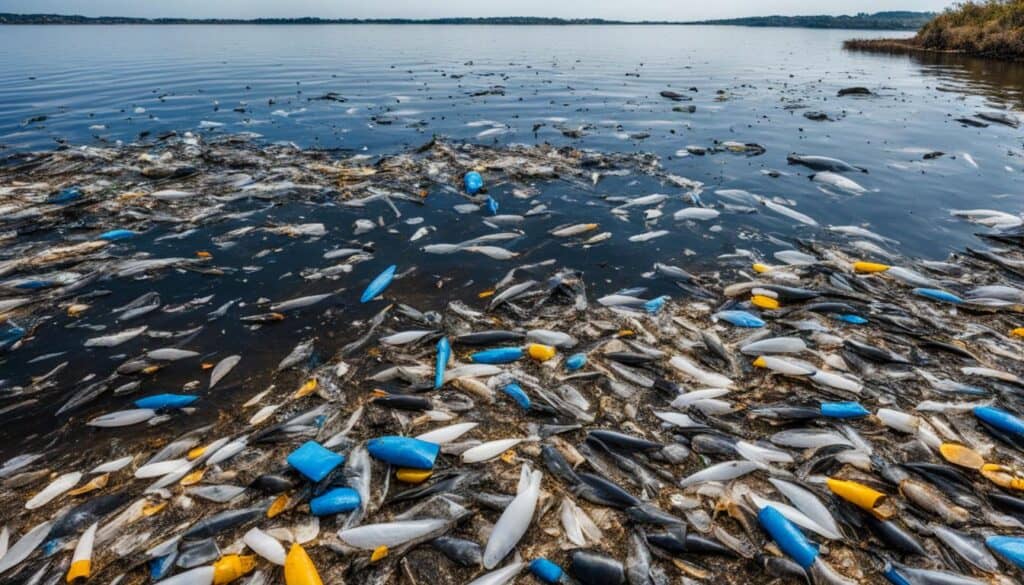

The spread of invasive species, such as the Nile perch, has also had a detrimental impact on the lake’s ecosystem. The introduction of these non-native species disrupts the natural balance and often leads to the extinction of native species.
The conservation of Lake Victoria’s natural resources is of vital importance to the region’s ecological stability and the sustenance of the communities that rely on its resources. – Dr. Jane Akinyi, Environmental Scientist
Efforts are underway to address these challenges and protect Lake Victoria’s ecosystem. Conservation organizations and government agencies are collaborating to implement sustainable fishing practices, manage water quality, and restore the ecosystem.
By implementing fishing regulations and promoting responsible fishing practices, it is possible to ensure the long-term sustainability of the lake’s fish stocks and preserve the livelihoods of the local fishing communities.
Water quality management programs aim to reduce pollution, protect water sources, and promote environmentally friendly practices in urban and agricultural areas surrounding the lake. These initiatives include improved waste management, wastewater treatment systems, and the promotion of sustainable agriculture practices.
Ecosystem restoration projects focus on rehabilitating the lake’s habitats, reintroducing native species, and controlling invasive species. These initiatives aim to restore the balance of the ecosystem and promote biodiversity.
Conservation and sustainable development are crucial for the long-term preservation of Lake Victoria and its surrounding communities. With concerted efforts and collaboration, it is possible to overcome the environmental challenges and ensure a thriving future for this remarkable African Great Lake.
Economic Importance and Tourism
Lake Victoria is not only a natural marvel but also a crucial contributor to the economies of the surrounding countries. The fishing industry, in particular, plays a vital role in providing employment and income for local communities.
The lake’s fishery produces an impressive one million tons of fish annually.
Aside from its economic significance, Lake Victoria is a highly sought-after tourist destination. Its vast expanse offers an array of activities, making it an ideal spot for boating, sport fishing, and wildlife viewing.
The scenic beauty of Lake Victoria, coupled with its unique wildlife and rich cultural heritage, attracts tourists from all over the world.
| Key Aspects | Opportunities |
|---|---|
| Boating | Boat rentals and guided tours |
| Sport Fishing | Specialized fishing trips and competitions |
| Wildlife Viewing | Safari tours and nature reserves |
The surrounding areas have embraced the lake’s tourism potential and have developed a robust infrastructure to cater to visitors. Hotels, resorts, and guided tour services provide comfort and convenience, ensuring an enjoyable experience for tourists exploring Lake Victoria.

Conclusion: Embark on an Adventure: Explore Lake Victoria, Africa’s Largest Freshwater Lake in Tanzania
Lake Victoria, the largest freshwater lake in Africa, is a remarkable natural wonder and a vital part of the African Great Lakes region. With its vast surface area and diverse wildlife, it captivates visitors and provides a livelihood for local communities through fishing and tourism.
However, Lake Victoria is not without its challenges. Environmental issues such as overfishing, pollution, and invasive species threaten the delicate balance of this ecosystem. It is crucial that we take proactive steps to preserve and restore the lake’s health and biodiversity.
Through sustainable fishing practices, proper water quality management, and the restoration of its fragile ecosystem, Lake Victoria can continue to be a valuable resource for the surrounding communities and a mesmerizing destination for travelers. It serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of nature and the importance of responsible stewardship for the African Great Lakes and beyond.
Related read: Exploring the Wealth of African Natural Resources